Basic Electrical Components ( Resistor, Capacitor and Inductor )
Basic Electrical Components
There are two types of
elements found in electric circuits:
1. passive elements and
2. active elements.
An
active element is capable of generating energy while a passive element is not .
Examples of passive element are resistors, capacitors and inductors. Typical
active elements include generators, batteries and operational amplifiers.
Resistor
A resistor is an electrical component that limits or regulates the flow of electrical current in an electronic circuit. Resistors can also be used to provide a specific voltage for an active device such as a transistor. |
| Fig-1: Resistor |
Resistance
The property of a substance which opposes the flow of electric current (or electricity) through it is called Resistance OR Resistance is the ability of a circuit which opposes current. Example of materials that show this property are Mica, Glass, Rubber, Wood etc.
The unit of resistance is OHM (Ω) where 1Ω = 1V/1A.
which is derived from the basic
electrical Ohm’s law = V = IR
Resistance of a
resistor depends on their length (l), resistivity (ρ) and its cross sectional
area (a) which is also known as laws
of resistance …
R = ρ (l/a) .
Types of Resistors
1. Linear Resistors
2. Non Linear Resistors
Linear Resistors
Those resistors, which values change with the applied voltage and temperature,
are called linear resistors. In other words, a
resistor, which current value is directly proportional to
the applied voltage
is known as linear resistors.
Generally, there are two types of resistors which have linear
properties.
a) Fixed Resistors
b) Variable Resistors
b) Variable Resistors
a)Fixed Resistors
Fixed Resistors : As the
name tells everything, fixed resistor is a resistor which has a specific value
and we can’t change the value of fixed resistors.
Types of Fixed resistors:
1. Carbon
Composition Resistors
2. Wire Wound Resistors
3. Thin Film Resistors
4. Thick Film Resistors
b) Variable Resistors : As the name indicates,
those resistors which values can be changed through a dial, knob, and screw or
manually by a proper method. In these types of resistors, there is a sliding
arm, which is connected to the shaft and the value of resistance can be changed
by rotating the arm.
Use of Variable Resistors :They are used in the radio receiver for volume control and
tone control resistance.
Following are the
further types of Variable Resistors:
1. Potentiometers 2. Rheostats 3. Trimmers
2. Non Linear Resistors : We know that,
nonlinear resistors are those resistors, where the current flowing through it
does not change according to Ohm’s Law but, changes with change in temperature
or applied voltage.
In addition, if the
flowing current through a resistor changes with change in body temperature,
then these kinds of resistors are called Thermisters.
If the flowing current
through a resistor change with the applied voltages, then it is called a
Varistors or VDR (Voltage Dependent Resistors).
Following are the
additional types of Non Linear Resistors.
1. Thermisters 2. Varisters (VDR) 3. Photo Resistor or Photo Conductive Cell or LDR
 |
| Fig-3 : Different Types of Resistor at a glance |
Uses / Application of Resistors :Practically, both
types of resistors (Fixed and Variable) are generally used for the following
purposes.
I. For Current control and limiting
II. To change electrical energy in the form of heat energy
III. As a shunt in Ampere meters
IV. As a multiplier in a Voltmeter
V. To control temperature
VI. To control voltage or Drop
VII. For protection purposes, e.g. Fusible Resistors
VIII. In laboratories
IX. In home electrical appliances like heater, iron, immersion rod etc.
X. Widely used in the electronics industries
I. For Current control and limiting
II. To change electrical energy in the form of heat energy
III. As a shunt in Ampere meters
IV. As a multiplier in a Voltmeter
V. To control temperature
VI. To control voltage or Drop
VII. For protection purposes, e.g. Fusible Resistors
VIII. In laboratories
IX. In home electrical appliances like heater, iron, immersion rod etc.
X. Widely used in the electronics industries
Measurement the value of a resistor ( Resistance):There are two ways to
measure the value of a resistor
1.Theoretical Measurement
and
2.Practical Measurement
In Theoretical
Measurement, we convert the color bands that are on the resistor body. For this
we also called 4 band resistor, 5 band resistor and so on. Each color is called
a band and each color has a numerical code that helps us to determine the
values of resistor. There are usually 12 color and each color has a value.
Fig-4 shows the color, their respective code. For example for black , the code
is zero (0) and for green , the code is Five (5) and so on. Normally four or
Five band resistors are available in market. If we consider a four band
resistor, that is 4 colors are drawn in its body, then by the following formula
we can easily calculate the value of the resistor.
Resistance ( R ) = AB×10C ± D %
Here D is called
Tolarance, which depends on the temperature.
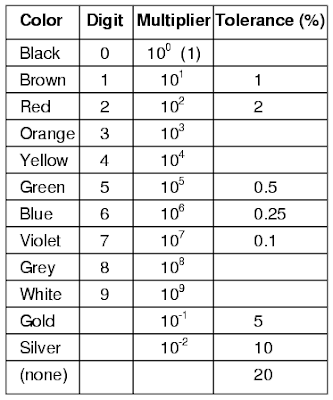 |
| Fig-4: Color Code |
If we consider a
resistor which has 4 band or color in its body and these colors are
Red, Green, Red, Gold
, then the value of the following resistor will calculate as follows:
Here the respective
code of the colors are
Red = 2
Green = 5
Red = 2
Gold = 5
Now if we put these
values to the above formula, we get,
R = 25 × 102 ±
5 % ohms (Ω )
R = 2500 ± 5 % ohms (Ω )
R = (2375 – 2625 ) Ω
For Five band
Resistor, the formula will be
Resistance ( R ) = ABC×10D ± E %
If we consider the
band as Red, Green, Black, Red, Gold then,
Here the respective
code of the colors are
Red = 2
Green = 5
Black = 0
Red = 2
Gold = 5
Now if we put these
values to the above formula, we get,
R = 250 × 102 ±
5 % ohms (Ω )
R = 25000± 5 % ohms (Ω )
R= (23750 – 26250) Ω
Practical Measurement : In Practical measurement , we use a ohm meter or
multimeter.
 |
| Fig-5: Measurement of Resistance usuing Multimeter. |
Characteristics of a resistor: It is very important
to know about the characteristics
any components to use it in our practical
life. Fig -6 shows the circuit and characteristics curve or I-V curve of a resistor.
 |
| Fig-6: Circuit and characteristics curve of a resistor |
-





you are clear my mind actually after reading your article i got clear my complete doubt. thanks for such easy understanding post. I also got some similar at here just for your info i post here link may be useful for future aspect What is a Resistor in electronics?
ReplyDeleteThank you for your comment...
DeleteVery good content...
ReplyDeleteRound spacers are small cylindrical components that are designed to separate two objects by a set distance. They are usually made of aluminum or stainless steel and are nonmagnetic. Their plain finish makes them easy to handle and are available in a range of sizes. For maximum efficiency, you should purchase these components in smaller quantities. They are available in various lengths, diameters, and weights. These small, yet versatile components are highly versatile and can be used in a variety of applications.
ReplyDelete